Title of project: Further studies of the validation and simultation of the Lake Urmia minerals exploration process, Report No. 2 (hydrogeochemistry and Site selection)
Executor of main plan: Dr Razyeh Lak
Executor of project: Dr Morteza Khalatbari Jafari
2020
In project report, the results of the magnetory data, the results of the network geochemical sampling and site selection of brines of Lake Urmia are study. Interpretation of the triple radiometric map revealed that radioactive elements (K, Th, U), are mainly concentrated on the edge of Lake Urmia. On the Islamic island located in the east of Lake, these elements have high contents could be attributed to volcanic composition of rocks. In NW of the Lake, U has high values that can be attributed to granite composition. Interpretation of radiometric data was also indicated that the basin thick in south of Lake is varies between 2500 to 3000 meters. In the middle part, thickness of the sedimentary basin reduces between800 to 1000 meters. In the northern part of Lake Urmia, the deep of the basin increases. Study of the magnetite stripes show two main lineations, with NW-SE strike which have been affected the sedimentary basin. As a result, horsts in the middle part and depression have been created in northern and southern sectors of Lake Urmia.
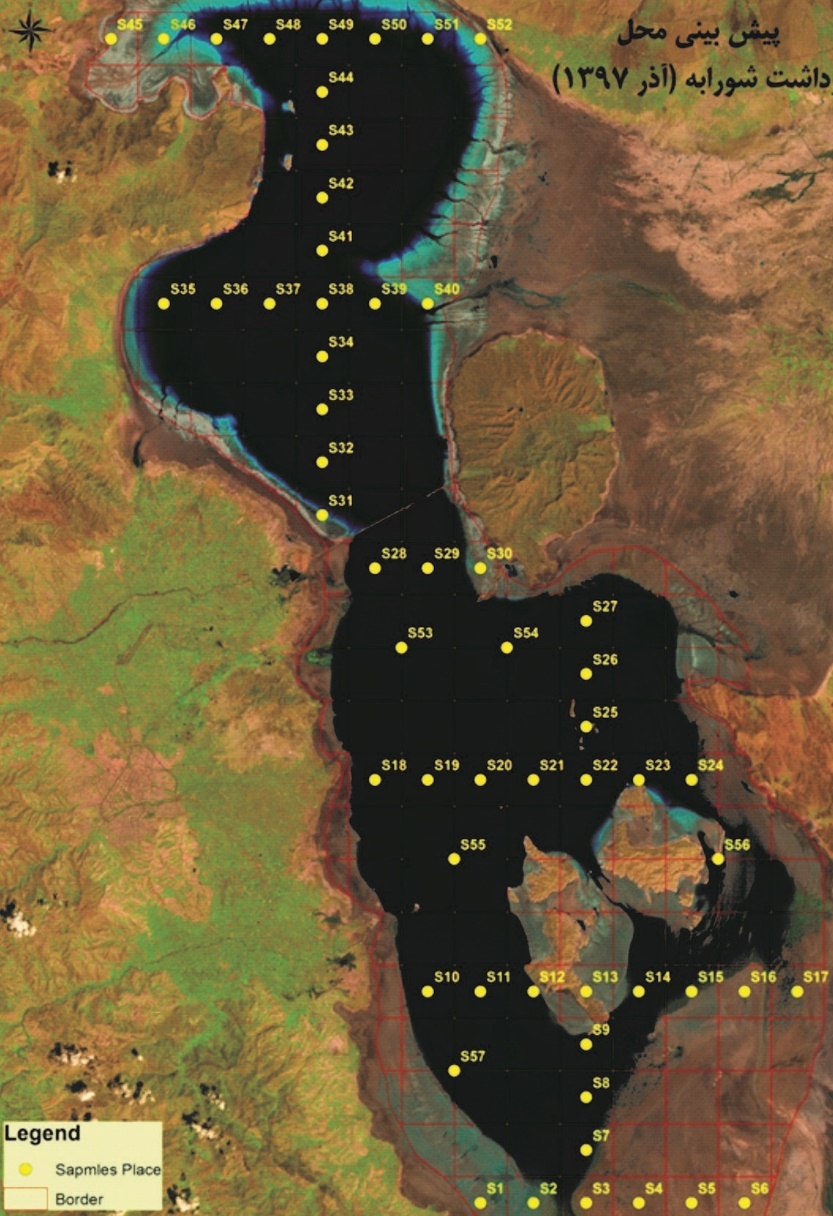
For hydro geochemistry studies of the brines of Lake Urmia, sampling was done at 5 km intervals. Base on the results of geochemical analysis, it seems that the dominant composition of brines in Lake Urmia is Mg-Cl. The distribution map of ions revealed that the economic minerals are more concentrated in the eastern edge of Lake Urmia. They include magnesium and potassium cations accompany by sulfate and chlorine anions. Our investigations in this project indicate that potential exploration of potassium deposits is possible in SE Lake Urmia (Sofi Chai sub-basin). Probability of exploration of magnesium deposits is more in Salmas sub-basin (Zola Chai).
Site selection studies in this project show that the deep of salt is higher in northern part of Lake Urmia. Maximum potential for exploration of magnesium and potassium reserves is projected in the north of the Lake. It is suggested that some impact drilling done in the coastal stripe, Because according to the theory of brine mixing, most economic elements concentrate in the coastal stripe. On the other hand, according to the sequence sedimentology, the order of deposition is carbonate-sulfate-chlorine-halite. So, potential for exploration of the potassium chloride components and magnesium chloride in deep of the Lake is more than the beach.
ارسال نظر برای این محصول مجاز نیست.
