
Petrology and geochemistry of the volcanic rocks in NE Abhar
Executor of project: Dr. Morteza Khalatbari Jafari
2016
In this thesis discussed, results of field, petrography and geochemical data from the Eocene volcanic rocks of the Aq Dagh area, northeast of Abhar. The studied volcanic rocks are a part of Karaj formation in southwest of Tarom range from Alborz structural zone. Most part of the study area formed of lavas and volcanoclastic rocks with basaltic andesite, andesite, trachy andesite, trachyte-trachy dacite, dacite and rhyolite-ignimbrite in composition, which are NW-SE direction. Based on field observation, it seems that the volcanic deposits erupted in five episode in aqueous to subaerial environments. All the volcanic series intruded by hypabyssal acidic intrusion. The intermediate-acidic volcanic rocks recorded evidences of magma mixing and mingling including basic-intermediate lithoclasts inside acidic groundmass and plagioclase phenocrysts, which show sieve texture, honeycomb structure, oscillatory zoning and dissolution margin. Also, acidic rocks have evidences of magma immiscibility. In geochemical discrimination magmatic diagrams, the studied lavas have high contents of K2O and K2O/Na2O and represent calk-alkaline, high-K calk-alkaline and shoshonitic characteristics. In binary diagrams, their arrangements, suggested fractional crystallization, which with Petrography studies, indication of differentiation of olivine, clinopyroxene, plagioclase, amphibole and Fe-Ti bearing minerals. In tectonomagmatic diagrams, the basic-intermediate samples plot in subduction field and in spider diagrams, they follow continental arc patterns. The acidic samples similar to S-type granitoides. The spider diagrams of acidic samples follow the patterns of peraluminous rhyolite and upper crust. REE and spider patterns of the volcanic rocks, display enrichments of LREE and LILE in relative to HREE and clear depletion of HFSE (such as Nb, Ta and Ti), which signifies of subduction zones.
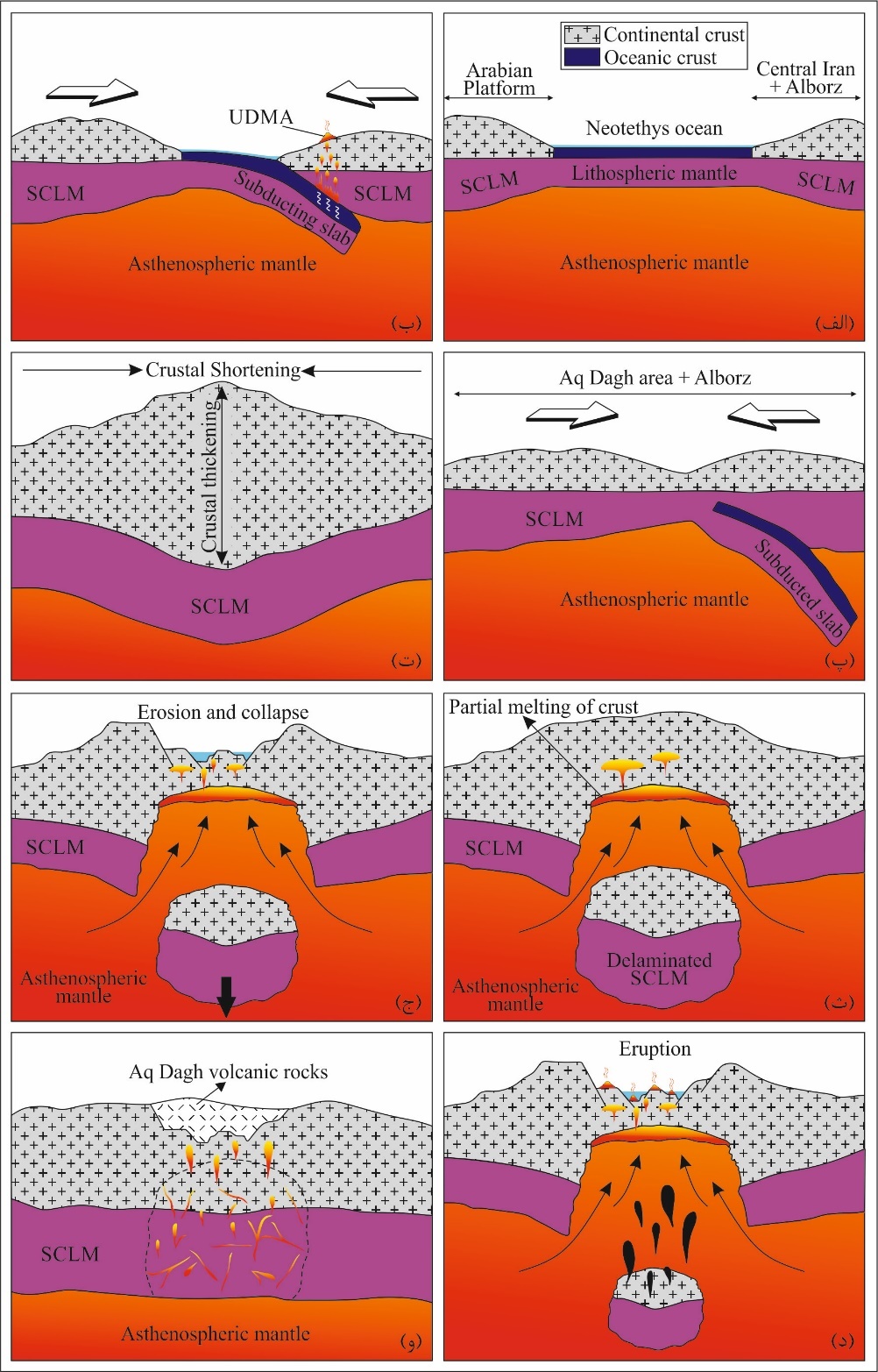
After collision of the Arabian platform to Iranian plate, and shortening of Alborz in Eocene, and subsequence lithospheric delamination, partial melting occur in sub continental lithospheric mantle (SCLM). The resulted melt accumulated in the upper crust and formed shallow magma chambers. Partial melting of the upper crust produced acidic magmas. It seems that mixing and mingling of basic melts released from SCLM with crustal components, had important role in generation of the magma of the volcanic rocks with basic-intermediate in composition.
ارسال نظر برای این محصول مجاز نیست.
