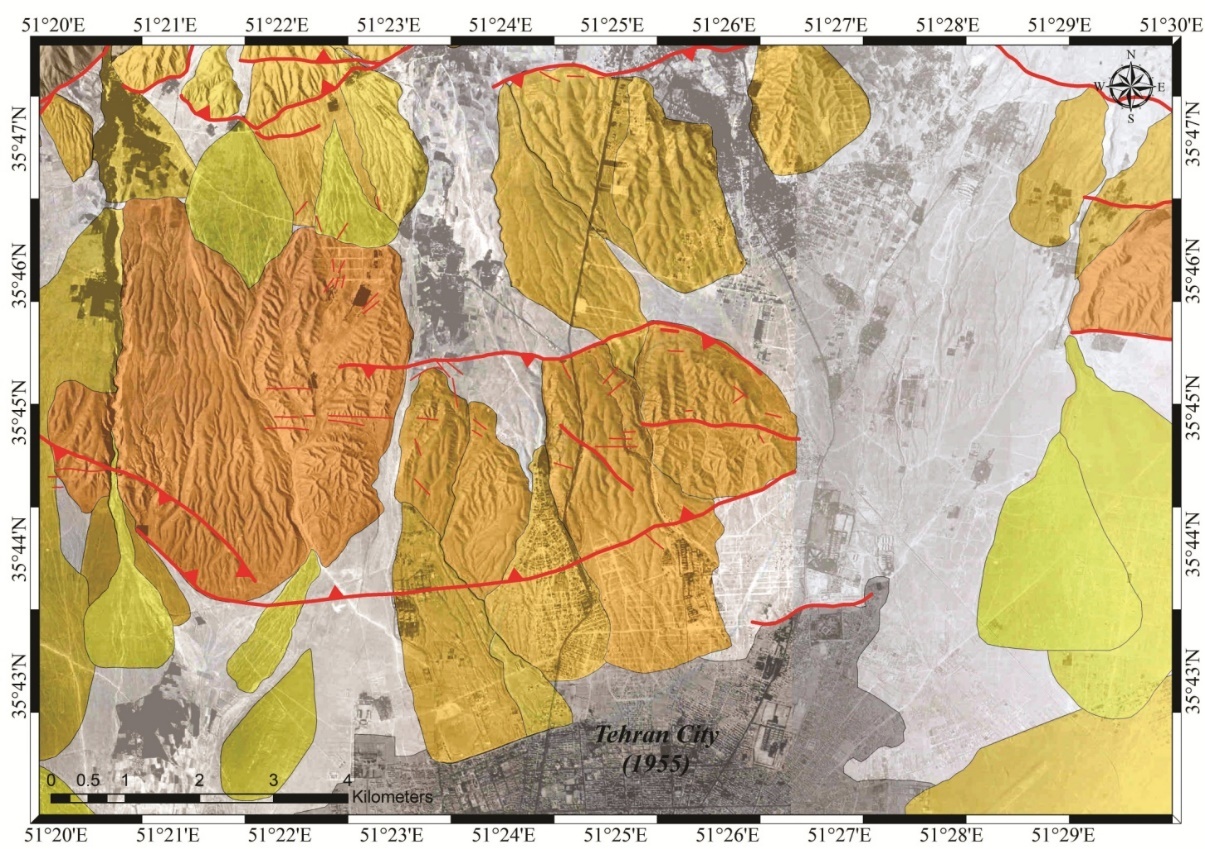


Active faulting and Quaternary deposits in Tehran plain
Executor of project: Dr. Morteza Talebia
2013
The scope of the study is part of the southern range of Central Alborz. Urban development of Tehran, as a metropolitan area, has caused a very large part of the study area to be covered by human construction, thus preventing visits and field operations in this area. For this reason, active tectonics studies have been performed based on various satellite imagery, such as 90-meter topographic data and aerial photographs (1: 50000). These images have been used to assess the position of faults and their displacements, fault mechanisms, and interpretation of alluvial fans in the study area. Preliminary observations have been confirmed by field studies, where geometric characteristics and the mechanism of the secondary faults, as well as characteristic of fan deposits has been studied directly in existing trenches and excavations.
In this research, especial attention has been done to location of the faults in populated area. Also, the thrust mechanism with the left component of the North Tehran fault has been reviewed and confirmed again. Different ag of alluvial deposits and their relation to faults are among other goals of this research
ارسال نظر برای این محصول مجاز نیست.
