
Petrogenesis and geochemistry of Bazman volcano
Executorof project: Dr. Jalil Ghalamghash
2016
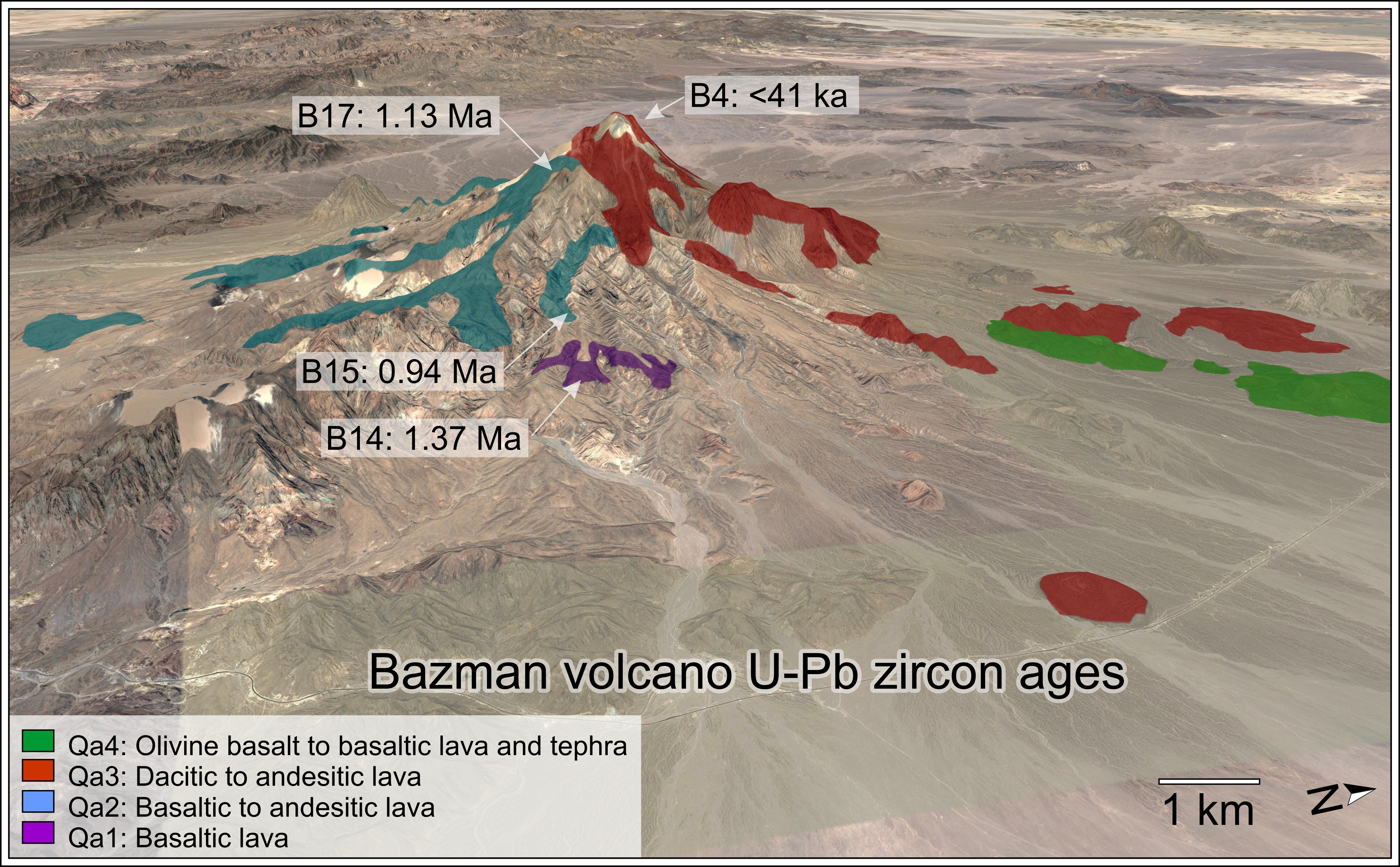
Bazman,Taftan and Kuh-e-Sultan volcanoes are related to magmatic arc zone of Makran- Chagay with east to west trend. This zone is located in southeastern of Iran and continued to southwest of Pakistan. Based on field studies, its volcanic rocks are classified into two groups Quaternary and Neogene volcanic rocks. The geological map of Bazman provided in this study, rock units are formed of basalt Ngv unit, Basalt, basaltic andesite and andesite Ngt unit, andesite unit Ngd,Qaurtz andesite unit Qt, andesite and andesite lithic crystal tuff unit Qa1, andesite, andesitic basalt, basaltic andesite and andesite lithic crystal tuff unit Qa2,andesite to trachyte andesite, and basaltic andesite unit Qig,basaltic andesite unit Qa3,andesitic basalt, olivine basalt and basaltic andesite. Andesites are mainly formed of minerals plagioclase, amphibole, pyroxene and quartz. The main observed textures are porphyritic, microporphyritic and seriate. Composition of plagioclase is andesine and oligoclase mainly. Pyroxenes are seen with low abundance and vary from medium to small sizes. Quartz is seen with low abundance and euhedral and subhedral formats.
Groundmass is composed of fine grain amphibole, pyroxene, plagioclase microlitic minerals and glass. Plagioclase, pyroxene and sometimes olivine minerals mainly exists in the basalt rocks. The main observed textures are porphyritic, microporphyritic and seriate. The composition of plagioclase phenocrysts mainly are labradorite and plagioclase microlites in the groundmass of andesine. Pyroxene minerals vary from phenocrysts to fine grain. There are olivine minerals in some samples. Groundmass is composed of fine grain minerals pyroxene, plagioclase microlitic, opaque minerals and glass. Pyroclastic studied samples, are mainly containing amphibole, plagioclase,opaque minerals and andesite rock fragments that present fractures in some parts. Groundmass in these samples is fine grain and consists of particulate that are undetectable or fine minerals and sometimes exhibit traction current structures. Petrographic and chemical naming of the samples often do not show an acceptable match. Number of samples that the petrographic nomenclature that consists of andesite, are located in the range of rhyolite and dacite within the chemical nomenclature for the major elements,that is probably due to nature of groundmass hidden particulate or fine minerals or silicification process. The volcanic rocks have calc-alkaline to thoeiite affinities. The origin of the magmas could be phlogopite-spinel lherzolite, and phlogopite-garnet lherzolite or mixture of both with high fraction of melting spinel. Neogene and Quaternary volcanic rocks have similar REE distribution patterns. These patterns show the relationship of LREE to HREEenrichment and indicate that, the origin of Bazman magma is a mantle rich in incompatible elements. The primitive mantle normalized based on Multi-elements diagrams; show a relatively high abundance of LILE relative to HFS incompatible elements and also negative anomalies of Nb and Ti. Negative anomaly of Nb and Ti elements in volcanic rocks shows that they made by subduction zone in the volcano. The tholeiitic nature of several samples from Bazman indicates that, his volcano close to subduction zone. The samples mainly are placed in the calc-alkaline arc basin and this basin is due to volcanic arc of the continent. Taftan and Kuh-e-Sultan volcanic rocks contain dacite, andesite and basaltic andesite.Their geodynamic condition and petrological characteristics show the acceptable match with Bazman.
ارسال نظر برای این محصول مجاز نیست.
